Knowing your body fat percentage is crucial for a comprehensive view of your health, transcending beyond mere weight or BMI. Body fat percentage reflects the actual amount of fat tissue in your body, providing a clearer picture of your health and fitness status. Unlike BMI, which calculates body mass based on height and weight without distinguishing between fat and muscle, body fat percentage offers a more precise assessment. This blog aims to guide you through the various methods to accurately calculate your body fat, helping you make informed decisions about your fitness goals and overall health management. By understanding and tracking your body fat percentage, you’re better equipped to tailor your diet and exercise plans effectively.
Methods of Measuring Body Fat
1. Skinfold Calipers
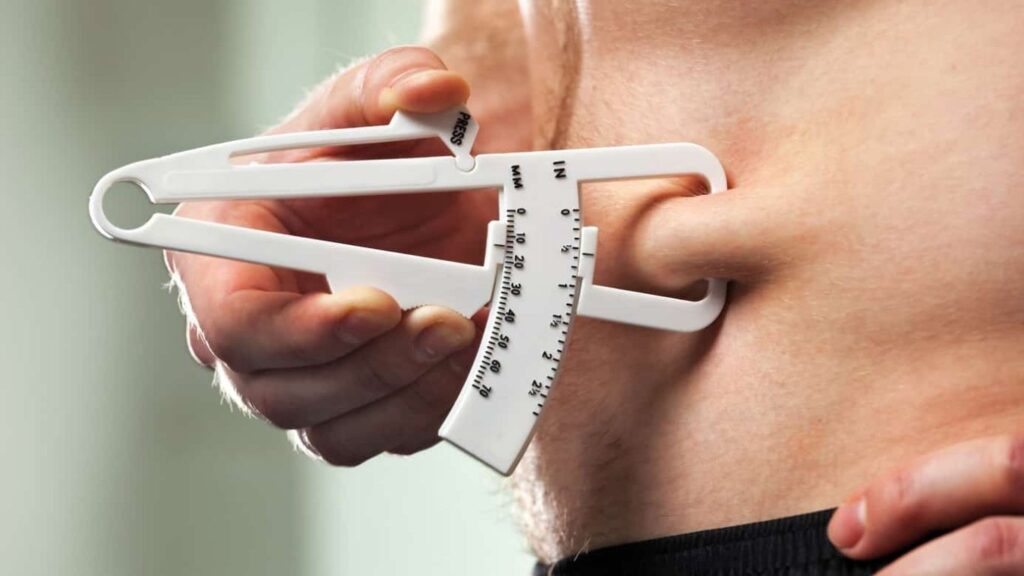
The skinfold caliper method involves measuring the thickness of skinfolds at specific body parts, such as the abdomen, thighs, and upper arms, to estimate body fat percentage. This technique is cost-effective and can be quite accurate when performed correctly. However, it is highly technique-sensitive, requiring precise measurement and consistency to ensure reliability. The accuracy also depends on the skill of the person conducting the assessment. Additionally, this method may not be suitable for very obese individuals, as the thickness of their skinfolds can exceed the limits of standard calipers, leading to less reliable measurements.
2. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
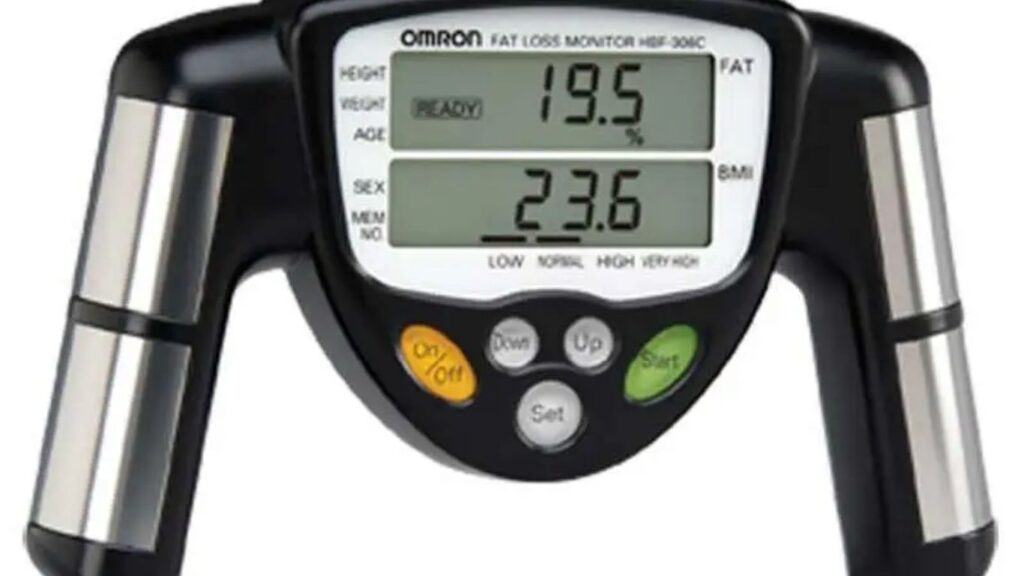

Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) utilizes a device that sends small electrical currents through the body to measure body composition. This technology is based on the principle that different body tissues conduct electricity at varying rates. Fat, having less water content, conducts electricity less effectively than muscle. BIA devices are widely accessible in fitness centers and come integrated into many personal bathroom scales, making them convenient for regular use. However, their accuracy can be influenced by factors such as hydration levels and recent meals, as both can alter the body’s electrical conductivity, leading to potential discrepancies in the readings.
3. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA Scan)
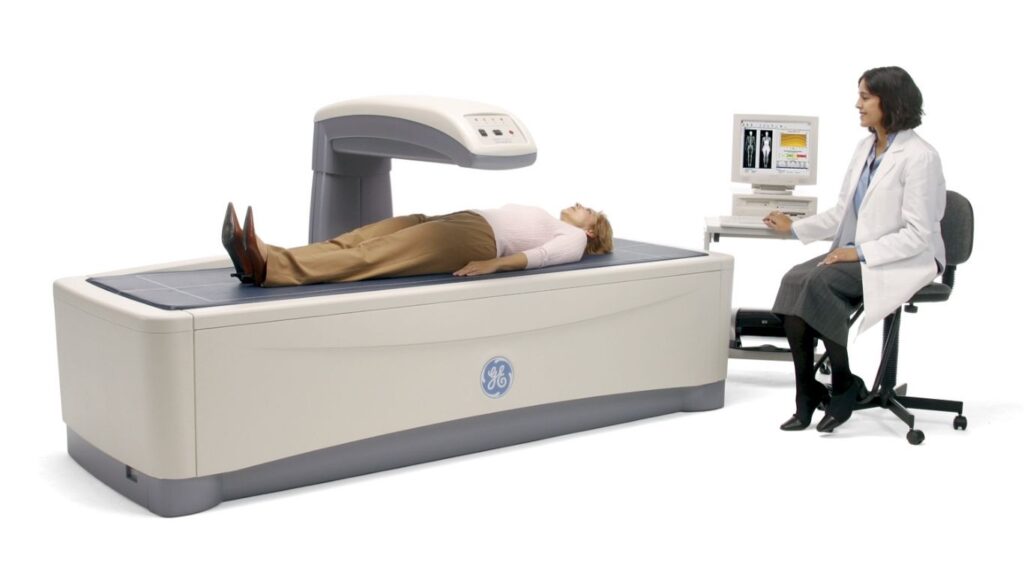
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) scans use X-ray technology to assess bone density and body composition, providing an in-depth analysis of fat distribution, muscle mass, and bone density. This method is highly valued for its precision and detail, offering one of the most accurate reflections of body composition available today. However, the primary limitations of DEXA scans lie in their cost and availability. They tend to be more expensive than other body fat measurement methods and are not as widely accessible, typically found in medical facilities or specialized clinics rather than standard fitness centers.
4. Hydrostatic Weighing
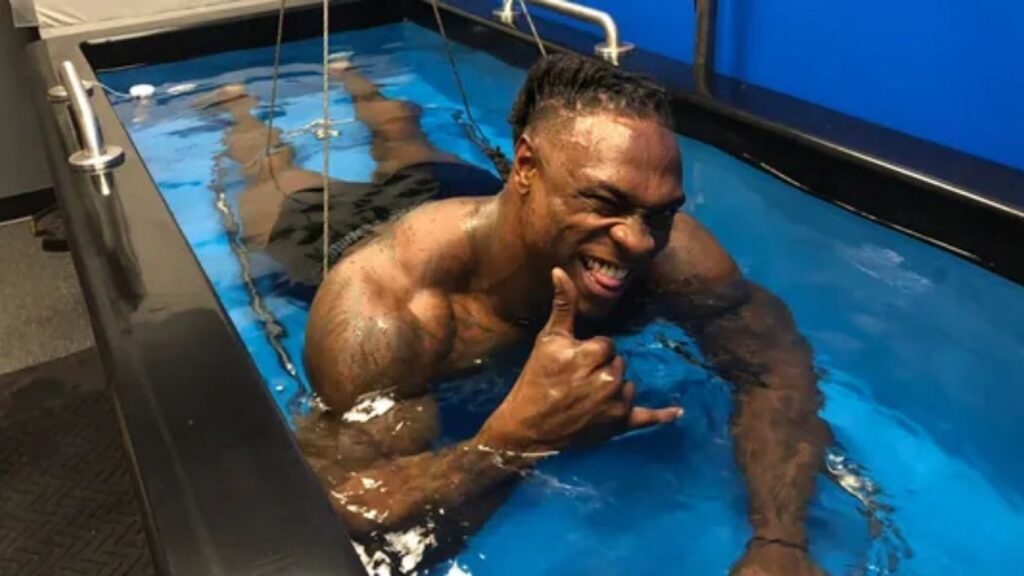

Hydrostatic weighing, also known as underwater weighing, is a method used to measure body density by assessing a person’s mass in water versus their mass in air. This technique is recognized for its high accuracy, making it a gold standard for measuring body fat percentage. The principle behind it is based on Archimedes’ principle, which states that the buoyant force on a submerged object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. However, the method’s accessibility is limited as it requires specialized equipment and facilities. Additionally, some individuals may find the process uncomfortable or challenging, particularly those who are not confident in water.
Choosing the Right Method for You
When selecting a method to measure body fat percentage, consider factors like accuracy, cost, convenience, and personal comfort. Accuracy is paramount for professionals such as athletes, who might opt for more precise methods like Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA Scans) or hydrostatic weighing to fine-tune their training and diet. These methods, while highly accurate, tend to be more expensive and less accessible.
For general fitness enthusiasts or those on a budget, Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) devices or skinfold calipers are more practical. These tools are cost-effective, widely available, and easy to use at home, providing a good balance between convenience and accuracy. Personal comfort is also crucial; for instance, those uncomfortable with underwater measurements might avoid hydrostatic weighing.
Ultimately, the choice depends on your specific health and fitness goals, budget considerations, and how frequently you plan to track your body fat percentage. Choosing the right tool can make your health monitoring both effective and comfortable.
Tips for Accurate Measurement
For the most accurate body fat measurements, consistency is key. Always measure at the same time of day, preferably in similar conditions, such as before breakfast and after using the restroom. This standardization minimizes variables that can affect your results, like food intake and water retention. Additionally, it’s crucial to meticulously follow the manufacturer’s instructions for any measuring device. Whether you’re using calipers, a bioelectrical impedance scale, or any other tool, correct usage ensures that the device’s technology accurately assesses your body fat percentage. Adhering to these guidelines will help you achieve reliable and repeatable results over time.
Conclusion
Accurately measuring your body fat percentage is a pivotal step towards a deeper understanding of your overall health and fitness. By exploring different methods and choosing one that suits your needs and circumstances, you can obtain precise insights into your body composition. Remember, consistency in how and when you measure, along with strict adherence to device instructions, will enhance the accuracy of your results. Regular monitoring of your body fat percentage not only helps in tracking progress but also in making informed adjustments to your diet and exercise regimen. Embrace this practice to actively manage and improve your health.
Also read: Understanding Body Fat Percentage: What It Tells Us About Our Health
