In recent years, a concerning trend has surfaced: a significant rise in cardiac arrests among young adults. Once primarily associated with older individuals, heart issues are now affecting people in their 20s, 30s, and 40s. This unexpected shift has raised alarm within the medical community, as younger populations are increasingly vulnerable to what was once considered an age-related problem. The spike in early-age cardiac arrests underscores the urgency to investigate its root causes and implement preventive strategies. Factors such as lifestyle habits, genetic predispositions, and undiagnosed heart conditions are thought to contribute to this growing issue. Understanding these causes and promoting heart-healthy behaviors is essential in addressing this emerging health crisis among young adults.
Rising Cases of Cardiac Arrests in Young Adults: Causes and Preventive Measures
Understanding Cardiac Arrests
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating, leading to a halt in blood flow to the brain and other vital organs. It is a medical emergency that, if not treated within minutes, can result in death. Although it is often confused with a heart attack, which is caused by a blockage in the arteries, cardiac arrest is typically triggered by an electrical disturbance in the heart.
While heart attacks can lead to cardiac arrest, other factors such as genetic predispositions, stress, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical conditions can also play a role, especially in young adults.
Causes of Cardiac Arrests in Young Adults

- Undiagnosed Heart Conditions Many young adults may have inherited heart conditions that remain undiagnosed until it is too late. Conditions like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), where the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick, can cause sudden cardiac arrest. Arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats, can also disrupt the heart’s normal rhythm, leading to a shutdown.
- High Stress Levels The modern world places enormous pressure on young adults, from job demands to financial stress and personal expectations. Chronic stress can increase the risk of heart problems, leading to high blood pressure, inflammation, and eventually, cardiac arrest. This heightened state of stress, combined with inadequate coping mechanisms, puts immense strain on the heart.
- Sedentary Lifestyles and Poor Diet A sedentary lifestyle, fueled by long hours of sitting at a desk or engaging in minimal physical activity, is a significant contributor to heart problems. Poor dietary habits, particularly the consumption of processed foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, can lead to obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol. These conditions increase the likelihood of heart complications, even at a young age.
- Substance Abuse Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and the use of recreational drugs have detrimental effects on heart health. Young adults who indulge in these behaviors are at a higher risk of cardiac arrest. For example, cocaine and other stimulants can trigger sudden arrhythmias, leading to cardiac arrest.
- Excessive Exercise Without Proper Health Monitoring While exercise is generally beneficial for heart health, overexertion without proper health monitoring can be dangerous. High-intensity sports or extreme workouts, especially in individuals with undiagnosed heart conditions, can precipitate cardiac arrest.
Preventive Measures
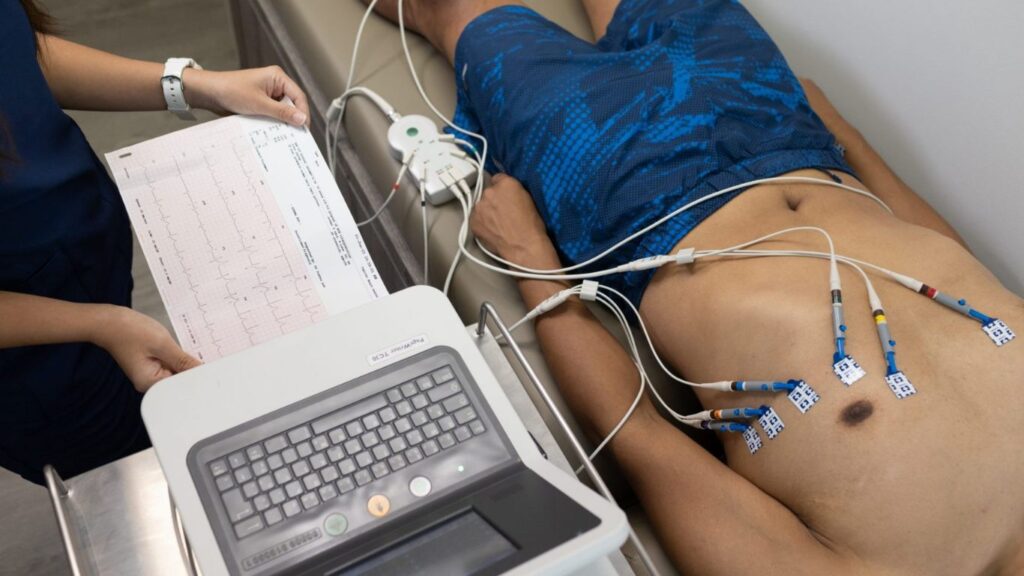
- Regular Health Check-ups One of the most effective ways to prevent cardiac arrest in young adults is through regular health check-ups. Early detection of heart abnormalities, such as arrhythmias or structural issues, can save lives. Routine blood pressure and cholesterol checks, along with heart screenings, should be prioritized, especially for those with a family history of heart disease.
- Stress Management Learning to manage stress is crucial for heart health. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce chronic stress. Additionally, adopting hobbies, maintaining a healthy work-life balance, and seeking support from family and friends can alleviate the mental pressures that contribute to heart problems.
- Adopting a Healthy Lifestyle Regular physical activity is vital for maintaining heart health. Young adults should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week. Activities like brisk walking, cycling, and swimming are excellent for cardiovascular fitness. Moreover, maintaining a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Avoiding Substance Abuse Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can drastically improve heart health. Additionally, steering clear of recreational drugs, especially stimulants like cocaine, is essential in preventing sudden cardiac events. Support from cessation programs and counseling can be helpful for individuals struggling to quit these habits.
- Listening to Your Body Many young adults may ignore warning signs such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or palpitations. It is essential to pay attention to these symptoms and seek medical attention when they occur. Early intervention can prevent a potential cardiac arrest.
Conclusion
The rising cases of cardiac arrests in young adults are a stark reminder that heart health is no longer a concern just for the elderly. With the right preventive measures—regular check-ups, stress management, healthy living, and avoiding harmful substances—young adults can significantly reduce their risk of cardiac arrest. Taking proactive steps now can ensure a long, healthy life with a well-functioning heart.
Also read: Genetic Factors vs. Lifestyle Choices: What’s Driving Early Cardiac Arrests?
