Uric acid is a natural waste product formed during the breakdown of purines, compounds found in certain foods and drinks. Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood, passes through the kidneys, and is expelled from the body through urine. However, when the body produces too much uric acid or the kidneys do not eliminate enough of it, high levels can accumulate in the bloodstream. This condition is known as hyperuricemia and can lead to various health issues, most notably gout. In this blog, we will discuss the signs and symptoms of high uric acid levels to help you recognize when something might be wrong.
Signs and Symptoms of High Uric Acid Levels
What is Hyperuricemia?
Before diving into the symptoms, it’s important to understand what hyperuricemia is. Uric acid is typically present in the blood at low levels. When the levels exceed 6.8 mg/dL, uric acid can crystallize and deposit in joints, tissues, and organs, leading to inflammation and various health problems. The most well-known complication of hyperuricemia is gout, a painful form of arthritis. However, high uric acid levels can also contribute to kidney stones and other kidney-related issues.
Signs and Symptoms of High Uric Acid Levels
High uric acid levels may not always cause noticeable symptoms right away. In many cases, hyperuricemia is only discovered during routine blood tests. However, as uric acid levels rise, symptoms can develop, often indicating more serious conditions like gout or kidney stones. Here are the common signs and symptoms of elevated uric acid levels.
1. Sudden Onset of Joint Pain (Gout Attack)
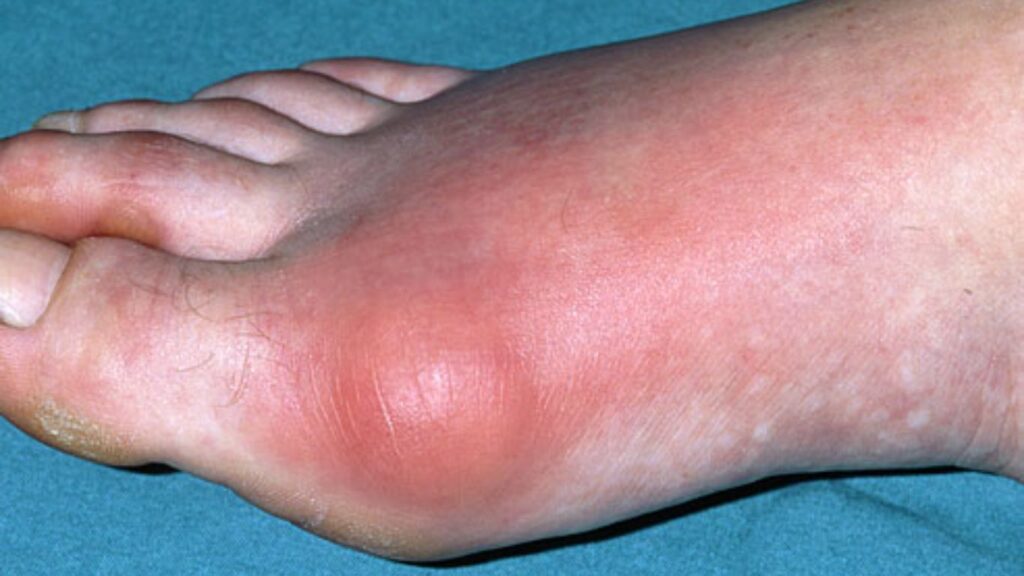
One of the hallmark symptoms of high uric acid levels is a gout attack, which often begins with sudden, intense pain in a joint. This pain usually strikes at night and can be so severe that even the weight of a bedsheet feels unbearable. The big toe is the most commonly affected joint, but gout can also impact the ankles, knees, wrists, fingers, and elbows. Gout attacks tend to occur in episodes, with periods of remission in between.
2. Swelling and Redness in Joints
Along with joint pain, swelling and redness are common signs of high uric acid levels. During a gout attack, the affected joint may become swollen, tender, and warm to the touch. The skin around the joint can appear red or purplish, and the swelling may cause limited mobility. This inflammation is due to the body’s immune response to uric acid crystals that form within the joint.
3. Tophi (Uric Acid Crystal Deposits)
Over time, if uric acid levels remain elevated, hard lumps known as tophi can form under the skin. These are collections of uric acid crystals that can develop in joints, cartilage, and soft tissues. Tophi are usually painless but can cause joint deformities and lead to chronic pain and stiffness if left untreated. They are often seen around the fingers, elbows, knees, and ears.
4. Frequent Urination or Pain During Urination
High uric acid levels can also affect kidney function. One of the early signs of uric acid buildup in the kidneys is frequent urination or discomfort while urinating. This occurs because the kidneys are struggling to filter excess uric acid from the blood. If uric acid crystals form in the kidneys, they can lead to the development of kidney stones, which cause sharp pain and urinary problems.
5. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are another potential complication of hyperuricemia. Uric acid stones form when excess uric acid crystallizes in the kidneys. Symptoms of kidney stones include severe pain in the lower back, sides, or abdomen, nausea, vomiting, and blood in the urine. Passing kidney stones can be extremely painful, and in some cases, medical intervention is required to remove them.
6. Fatigue and Malaise
Chronic hyperuricemia can lead to feelings of fatigue and general malaise. This is partly due to the inflammation caused by uric acid crystals in the joints and kidneys, which can leave the body feeling run down. The pain and discomfort associated with gout or kidney stones can also disrupt sleep, contributing to exhaustion and a reduced quality of life.
7. Increased Risk of Hypertension and Heart Disease
Although not a direct symptom, high uric acid levels have been linked to an increased risk of hypertension (high blood pressure) and cardiovascular diseases. Uric acid may contribute to the hardening of arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke. While these conditions may not show immediate symptoms, it’s crucial to monitor uric acid levels to reduce potential long-term complications.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the above symptoms, especially recurrent joint pain or the sudden onset of gout attacks, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Blood tests can help determine whether your uric acid levels are elevated. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the progression of hyperuricemia to more severe conditions, such as chronic gout or kidney damage.
Conclusion
High uric acid levels can lead to painful and debilitating conditions like gout and kidney stones if left untreated. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of elevated uric acid levels is key to managing hyperuricemia and preventing long-term health problems. If you suspect that your uric acid levels may be high, consult with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that may include lifestyle changes, medications, and dietary adjustments. By taking proactive steps, you can maintain healthy uric acid levels and avoid the complications associated with hyperuricemia.
Also read: 8 Daily Habits That Can Cause Internal Inflammation
