Folliculitis is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when hair follicles become inflamed, leading to red, itchy, and sometimes painful bumps on the skin. While folliculitis can affect anyone, certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition. In this blog, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and risk factors of folliculitis, helping you better understand how to prevent and manage this skin issue.
Understanding Folliculitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Risk Factors
What is Folliculitis?
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles, the tiny pockets in the skin from which hair grows. This condition can occur anywhere on the body where hair is present, but it is most commonly found on the face, neck, scalp, chest, back, buttocks, and thighs. Folliculitis can range from a mild, superficial infection to a more severe and deeper form of inflammation that may lead to scarring or permanent hair loss.
There are two primary types of folliculitis:
- Superficial Folliculitis: This form affects only the upper part of the hair follicle. It is usually less severe and heals on its own with proper care.
- Deep Folliculitis: This form involves the entire hair follicle and can lead to more significant symptoms and complications. Deep folliculitis often requires medical treatment to prevent scarring and further infection.
Causes of Folliculitis
Several factors can cause or contribute to the development of folliculitis. Understanding these causes can help in identifying potential triggers and taking steps to prevent the condition from occurring.
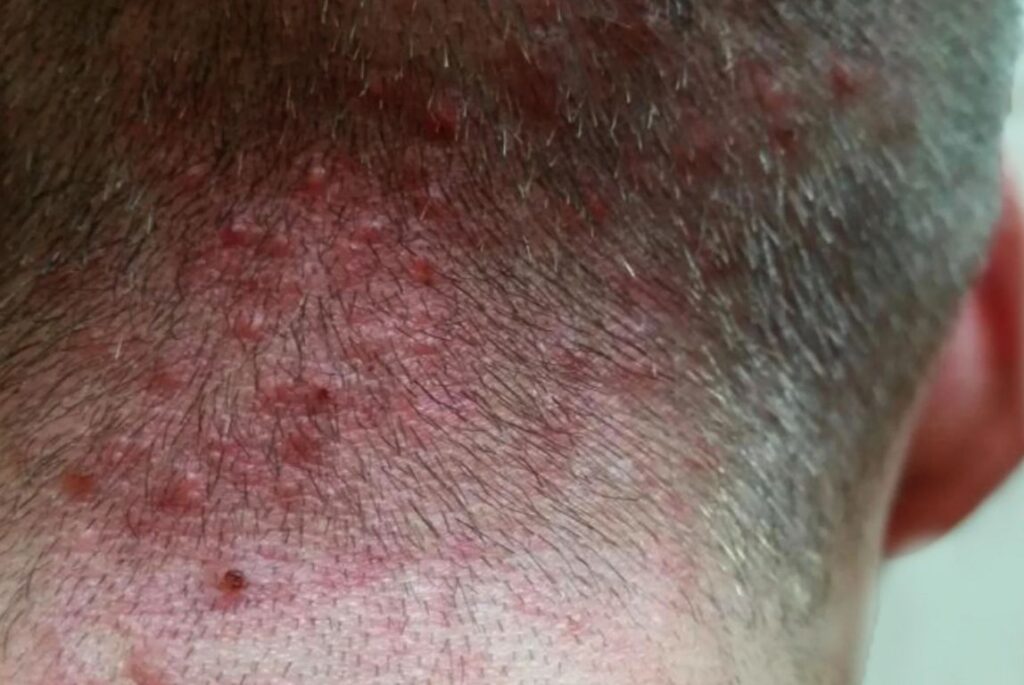
Bacterial Infections
The most common cause of folliculitis is a bacterial infection, typically by Staphylococcus aureus. These bacteria are normally present on the skin but can cause infection when they enter the hair follicles through small cuts, abrasions, or damage to the skin. This type of folliculitis is known as bacterial folliculitis and can lead to the formation of red, pus-filled bumps.
Fungal Infections
Fungal folliculitis is caused by an overgrowth of yeast or fungi, such as Malassezia or Candida. These microorganisms can proliferate in warm, moist environments, making areas like the groin, armpits, and under the breasts particularly susceptible. Fungal folliculitis often presents as small, red, itchy bumps and may require antifungal treatment.
Viral Infections
Certain viral infections, such as herpes simplex virus (HSV), can lead to viral folliculitis. This form of folliculitis is typically more painful and may be accompanied by fluid-filled blisters. HSV-related folliculitis usually occurs around the mouth or genitals and requires antiviral medication for treatment.
Physical Irritation
Physical irritation of the hair follicles is another common cause of folliculitis. Shaving, waxing, and wearing tight clothing can all cause friction and damage to the hair follicles, leading to inflammation. This type of folliculitis, often referred to as “razor bumps” or “barber’s itch,” is common on the face, neck, and legs.
Occlusion and Sweating
The blockage of hair follicles due to occlusive products (such as heavy lotions, oils, or makeup) or excessive sweating can create an environment where bacteria or fungi thrive. This can lead to the development of folliculitis, especially in areas where the skin is prone to moisture and friction.
Autoimmune and Dermatologic Conditions
In some cases, underlying autoimmune or dermatologic conditions, such as psoriasis or eczema, can lead to folliculitis. These conditions can cause chronic inflammation of the skin, making the hair follicles more susceptible to infection and irritation.
Symptoms of Folliculitis
The symptoms of folliculitis can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
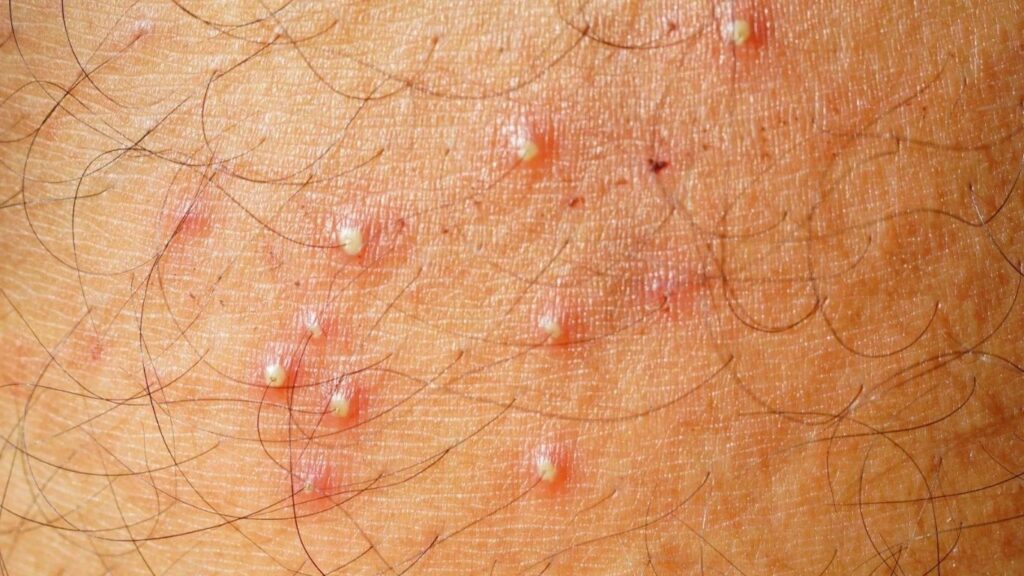
Red Bumps or Pimples
The most noticeable symptom of folliculitis is the appearance of red bumps or pimples around the hair follicles. These bumps may be filled with pus and can develop into larger, more painful sores if left untreated.
Itching and Burning
Folliculitis often causes itching and a burning sensation in the affected area. This can be particularly uncomfortable, especially in areas where the skin is sensitive or prone to friction.
Tenderness and Pain
As the inflammation progresses, the affected area may become tender to the touch. Pain may also occur, especially if the folliculitis is deep or if the hair follicles become infected.
Crusting or Scabbing
In more severe cases of folliculitis, the affected area may develop crusts or scabs as the sores heal. This can lead to scarring or hyperpigmentation if not properly managed.
Swelling and Abscess Formation
In cases of deep folliculitis, the inflammation may cause swelling around the affected area, leading to the formation of abscesses. These abscesses may require medical intervention, such as drainage or antibiotics, to prevent further complications.
Risk Factors for Folliculitis
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing folliculitis. Being aware of these risk factors can help you take preventive measures to avoid the condition.
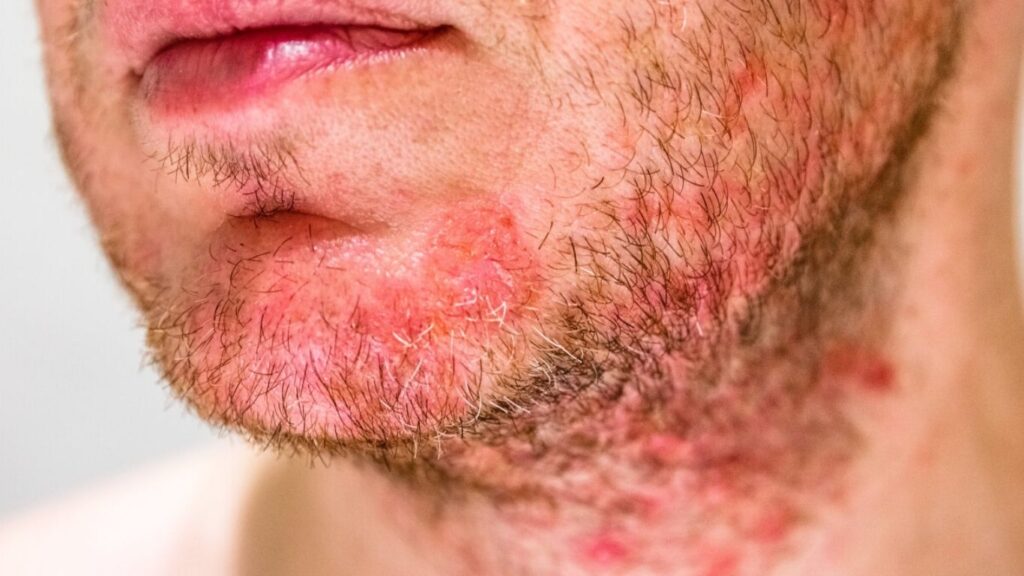
Personal Hygiene
Poor personal hygiene can contribute to the development of folliculitis. Failing to keep the skin clean, especially after sweating or using occlusive products, can lead to clogged hair follicles and bacterial or fungal growth.
Shaving and Hair Removal
Frequent shaving or improper hair removal techniques can cause micro-injuries to the skin, increasing the risk of folliculitis. Using dull razors, shaving against the grain, or waxing can all contribute to follicle irritation and inflammation.
Tight Clothing
Wearing tight clothing, especially in hot and humid conditions, can trap sweat and moisture against the skin. This creates an environment conducive to bacterial and fungal growth, leading to folliculitis.
Existing Skin Conditions
Individuals with existing skin conditions, such as acne, eczema, or dermatitis, are at a higher risk of developing folliculitis. These conditions can compromise the skin’s barrier function, making it more susceptible to infection.
Hot Tubs and Pools
Using improperly maintained hot tubs or swimming pools can expose the skin to bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which can cause a type of folliculitis known as “hot tub folliculitis.” This condition typically appears within a few days of exposure and is characterized by red, itchy bumps.
Weakened Immune System
A weakened immune system, whether due to chronic illness, medication, or stress, can increase the risk of folliculitis. Individuals with compromised immune function are less able to fight off infections, making them more susceptible to skin conditions like folliculitis.
Conclusion
Folliculitis is a common yet preventable skin condition that can cause discomfort and inconvenience. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and risk factors associated with folliculitis, you can take proactive steps to protect your skin and maintain healthy hair follicles. With proper care and attention, you can reduce the likelihood of developing folliculitis and ensure your skin remains healthy and irritation-free.
Also read: How Your Eating Habits Affect Your SkinAlso read:
