Selenium is an essential trace mineral that, despite its requirement in only small amounts, plays a significant role in various bodily functions, particularly in supporting the immune system. It is vital for the production and activity of selenoproteins, which are crucial for reducing oxidative stress and modulating immune responses. By neutralizing harmful free radicals and enhancing the function of immune cells such as T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells, selenium contributes significantly to maintaining a robust immune system. Adequate intake of selenium is therefore crucial for overall health and the prevention of various immune-related diseases. Ensuring a balanced diet with sufficient selenium can help bolster the body’s natural defenses.
The Vital Role of Selenium in Boosting Your Immune System
The Science Behind Selenium and Immunity
Selenium’s role in immunity primarily revolves around its function as an antioxidant and its incorporation into selenoproteins. These proteins are integral to many physiological processes, including immune responses. Specifically, selenoproteins such as glutathione peroxidases help reduce oxidative stress by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage cells and weaken the immune system if left unchecked.
Oxidative stress is linked to increased inflammation, impaired immune responses, and the development of various diseases, making selenium’s antioxidant properties crucial for maintaining immune health.
How Selenium Supports Immune Cells
Selenium influences several key components of the immune response, including the activity of various immune cells like T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. These cells are essential for identifying and combating infections, thus reinforcing the body’s defense mechanisms. Research has shown that selenium deficiency can lead to immunosuppression, reducing the body’s ability to fight off microbial and viral infections.
Moreover, selenium plays a role in enhancing the proliferation of T and B lymphocytes, which are vital for adaptive immunity. This adaptive response is crucial for the body to remember and effectively combat pathogens it has encountered before. Selenium also supports the function of neutrophils, which are the first responders to infection, helping to protect the body from the early stages of microbial invasion.
Selenium and Inflammation Control
Inflammation is a crucial immune response to infection or injury, but when it becomes chronic, it can contribute to various health issues, including autoimmune diseases. Selenium plays a key role in regulating the immune system’s inflammatory response by ensuring that inflammation is controlled and does not become excessive. This regulation helps prevent chronic inflammation, which is linked to a range of conditions like heart disease, arthritis, and other inflammatory-based illnesses. By maintaining this balance, selenium supports a healthier immune system that effectively responds to threats without causing additional harm to the body.
Selenium and Viral Infections
Viral infections present a significant challenge to the immune system, and selenium plays a crucial role in enhancing the body’s defense against these threats. Studies have shown that a deficiency in selenium can worsen the severity of viral infections, including influenza and HIV. Conversely, maintaining adequate selenium levels has been linked to a reduced risk of these infections and improved outcomes for those affected. Selenium supports the immune system by boosting the activity of immune cells and enhancing the body’s ability to counteract viral invaders, making it a vital nutrient for antiviral defense and overall immune resilience.
Dietary Sources of Selenium
Ensuring sufficient selenium intake through diet is crucial, given its importance in immune function. Foods rich in selenium include Brazil nuts, which are exceptionally high in this mineral, as well as seafood like tuna, sardines, and halibut. Other sources include eggs, chicken, sunflower seeds, and shiitake mushrooms. The selenium content in these foods can vary based on soil composition and environmental factors, particularly for plant-based sources.
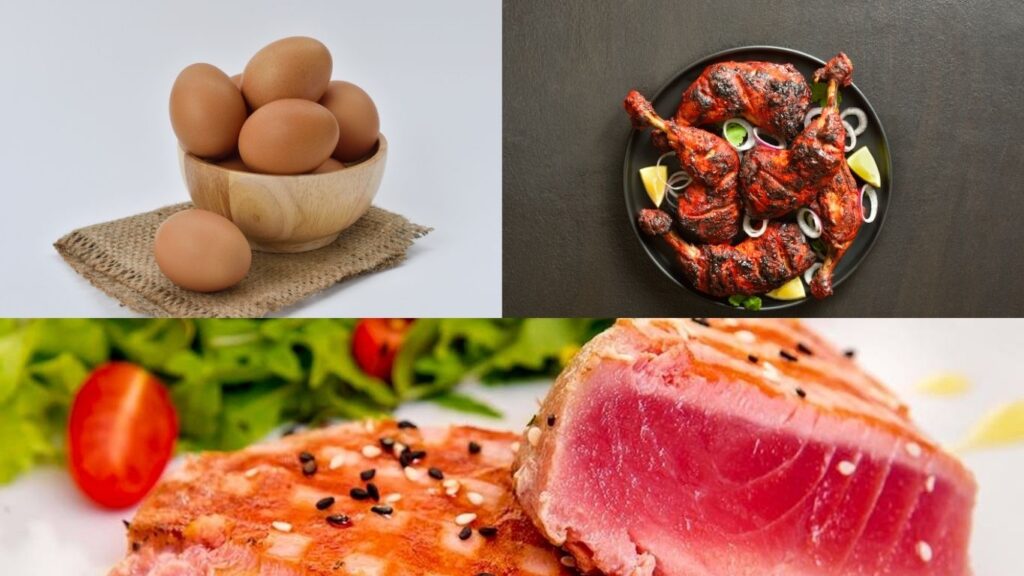

For individuals who may struggle to get enough selenium from diet alone, supplementation can be considered, but it should be approached with caution due to the U-shaped dose-response curve of selenium. Both deficiency and excess of selenium can lead to health issues, so it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation.
Conclusion
Selenium is a vital nutrient for immune health, playing a crucial role in protecting the body against oxidative stress, supporting immune cell function, and modulating inflammation. By ensuring adequate selenium intake through a balanced diet or careful supplementation, individuals can enhance their immune system’s resilience against infections and chronic diseases.
Incorporating selenium-rich foods into your daily diet is a proactive way to bolster your immune defenses, making it an essential component of overall health and wellness. For those with specific health concerns or dietary restrictions, consulting with a healthcare provider to determine the right approach to selenium intake is recommended.
Read more: 7 Signs of Selenium Deficiency in the Body
