Selenium is a crucial trace mineral that supports several essential body functions, including bolstering the immune system, regulating thyroid hormones, and protecting cells from oxidative damage. Despite its significance, a deficiency in selenium can arise, leading to various health concerns. The body’s inability to function optimally without sufficient selenium can manifest in several ways, such as impaired immune response, thyroid dysfunction, and increased vulnerability to oxidative stress. Recognizing the selenium deficiency symptoms early on can help in addressing the deficiency and maintaining overall health. Understanding how selenium deficiency impacts the body is key to preventing its associated health issues.
7 Signs of Selenium Deficiency in the Body
1. Impaired Immune Function
Selenium is crucial for maintaining a robust immune system. It aids in the production of glutathione peroxidase, an antioxidant enzyme that protects cells from oxidative stress. When selenium levels are low, your body’s ability to fight infections and recover from illness is compromised, leading to frequent sickness and prolonged recovery times. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with chronic diseases, may experience more severe symptoms of selenium deficiency.
2. Hair Loss
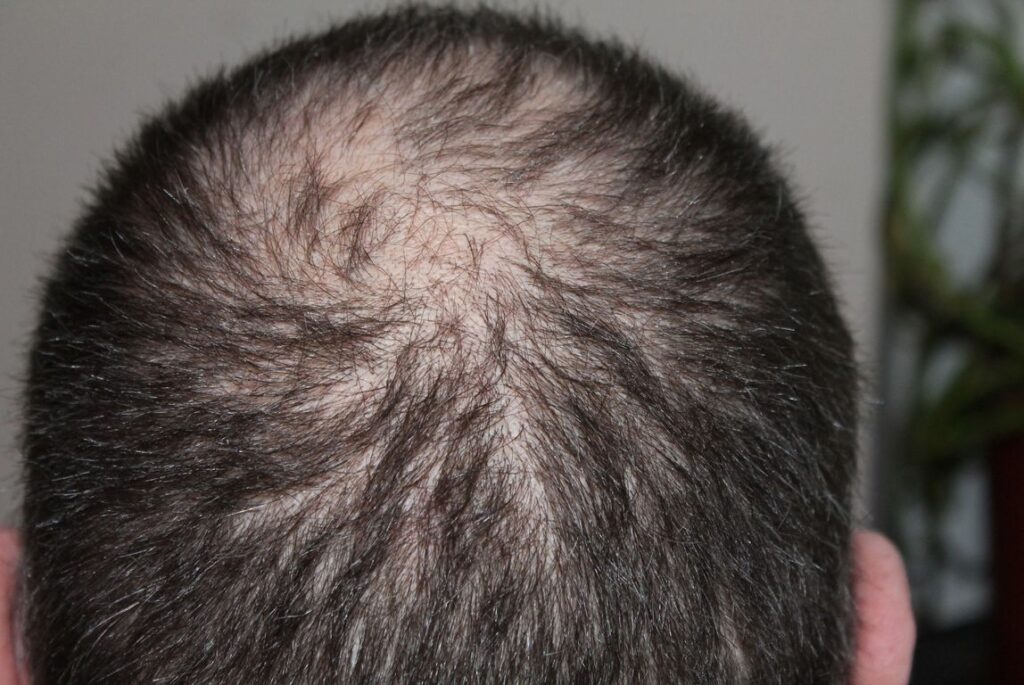
Hair loss is a common sign of selenium deficiency, often linked to its role in thyroid hormone metabolism. Selenium is necessary for the conversion of thyroxine (T4) to the more active triiodothyronine (T3), which regulates many metabolic processes, including hair growth. A deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism, which is characterized by symptoms such as thinning hair and overall hair loss.
3. Cognitive Impairment and Mental Fog
Selenium is vital for brain health due to its antioxidant properties, which protect brain cells from oxidative damage. Low selenium levels can lead to mental fog, difficulty concentrating, and memory issues. These cognitive symptoms are particularly concerning in older adults, as selenium deficiency may exacerbate age-related cognitive decline.
4. Reproductive Health Issues
Selenium deficiency can negatively impact reproductive health in both men and women. In men, it can lead to reduced sperm motility, contributing to infertility. In women, low selenium levels have been associated with complications during pregnancy, such as miscarriages, preeclampsia, and gestational diabetes. Ensuring adequate selenium intake is essential for maintaining reproductive health and successful pregnancy outcomes.
5. Muscle Weakness and Fatigue
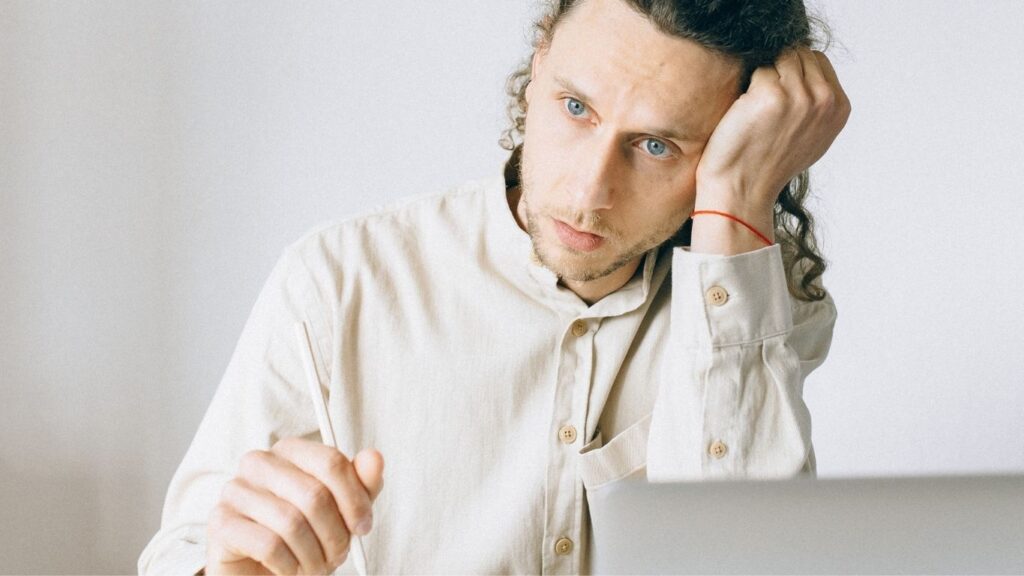

Muscle weakness and fatigue are common symptoms of selenium deficiency due to its role in mitochondrial function, the powerhouse of the cell. Without sufficient selenium, the mitochondria cannot produce energy efficiently, leading to muscle weakness, chronic fatigue, and reduced exercise tolerance. This can be particularly debilitating for those who are physically active or have high energy demands.
6. Thyroid Dysfunction
Selenium is critical for thyroid function, as it is involved in the production and regulation of thyroid hormones. A deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. Symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and a sluggish metabolism. Addressing selenium deficiency can help restore normal thyroid function and alleviate these symptoms.
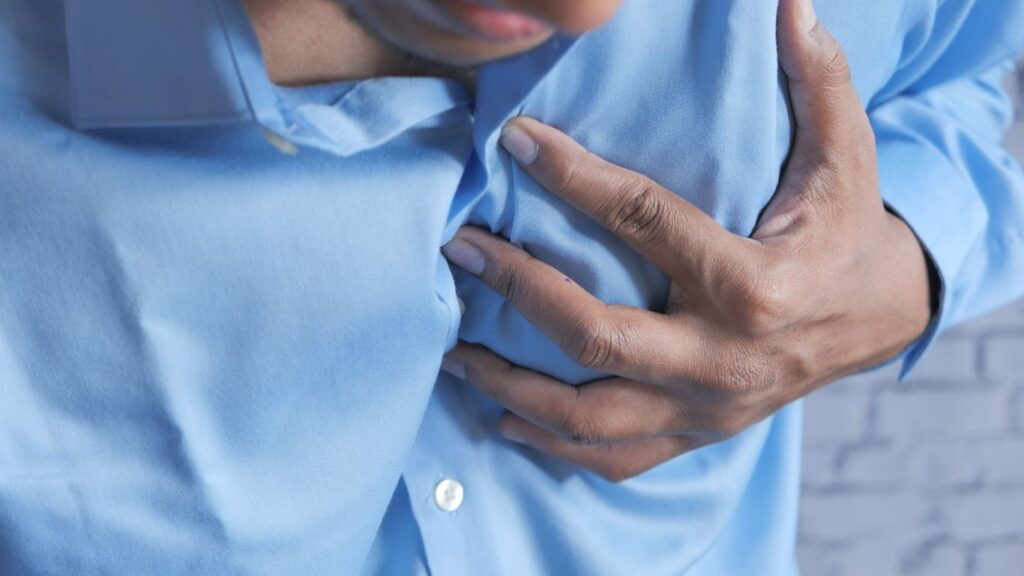
7. Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases
Low selenium levels have been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Selenium deficiency can lead to higher oxidative stress and inflammation, contributing to the development of atherosclerosis, heart disease, and other cardiovascular conditions. Ensuring adequate selenium intake can help protect the heart by reducing oxidative stress and supporting overall cardiovascular health.

How to Address Selenium Deficiency
To address selenium deficiency, incorporate selenium-rich foods like Brazil nuts, seafood, organ meats, eggs, and grains into your diet. While dietary sources are ideal, supplements can be beneficial if needed. However, it’s crucial not to exceed the recommended daily intake, as too much selenium can be toxic. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential before starting any supplementation, especially if you suspect a deficiency, to ensure you are meeting your nutritional needs safely and effectively. This approach helps maintain balanced selenium levels, promoting overall health and preventing potential toxicity.
Conclusion
Identifying the signs of selenium deficiency is essential for safeguarding your health. Ensuring adequate selenium intake through diet or supplements can help avert the harmful effects linked to its deficiency. Should you notice any symptoms, consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Balanced nutrition is fundamental in preventing deficiencies and supporting overall wellness, as it provides the necessary nutrients your body needs to function optimally. Regularly including selenium-rich foods like Brazil nuts, seafood, and whole grains in your diet can help maintain healthy selenium levels, contributing to your overall health and vitality.
Read more: Zinc Supplementation: When and Why It Becomes Necessary
