Heart disease stands as the foremost cause of death globally, accounting for a significant proportion of mortality each year. The condition encompasses a range of cardiovascular complications, including coronary artery disease, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes. As individuals cross the threshold of 40, the risks associated with heart disease escalate due to natural aging processes, changes in metabolism, and potential accumulations of unhealthy lifestyle practices. This makes heart health exceptionally critical past this age. It is vital to recognize the implications of heart disease and take proactive steps towards prevention and management to mitigate these risks. Emphasizing heart health after 40 is not just advisable but essential for longevity and improved quality of life.
Strategies for Preventing and Managing Heart Disease After Age 40
Key Risk Factors for Heart Disease After 40
Understanding the risk factors for heart disease is crucial for prevention and management, particularly after age 40. Here are some common contributors:
- Genetic Predisposition: Genetics play a significant role in an individual’s susceptibility to heart disease. Those with a family history of cardiovascular issues are more likely to encounter similar problems, suggesting that genetics can predispose individuals to heart conditions.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Smoking: One of the most harmful habits, smoking damages the lining of the arteries, leads to the buildup of plaque, and increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to the development of heart disease by leading to weight gain, decreased heart function, and poor blood circulation.
- Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and processed foods can raise cholesterol levels and contribute to artery blockage, thereby increasing heart disease risk.
- Health Conditions:
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Forces the heart to work harder than normal, leading to damage over time.
- High Cholesterol: Leads to plaque build-up in the arteries, narrowing them and making heart attack or stroke more likely.
- Diabetes: Increases the risk of heart disease significantly as high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure, temporary spikes in these can cause damage to the cardiovascular system over time, exacerbating other risk factors.

Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Heart Health
1. Nutritional Adjustments
A balanced diet is essential for heart health, especially after age 40. Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins which provide vital nutrients and fiber. These foods help manage weight, reduce cholesterol, and stabilize blood sugar levels. It’s crucial to limit intake of saturated fats, added sugars, and salts, as these can increase blood pressure and heart disease risk. Prioritizing heart-healthy foods while minimizing harmful ones can significantly improve cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
2. Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise significantly boosts heart health by improving blood circulation, reducing blood pressure, and strengthening the heart muscle. For individuals over 40, it’s advisable to engage in a mix of aerobic activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, and strength training to maintain muscle mass and metabolic rate. Additionally, flexibility and balance exercises such as yoga or Tai Chi can enhance coordination and prevent falls, making them ideal for maintaining overall cardiovascular and physical health as one ages.
3. Weight Management
Obesity significantly raises the risk of heart disease by straining the heart, elevating blood pressure, and increasing cholesterol levels. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential, along with monitoring portion sizes and choosing nutrient-rich foods to combat obesity effectively.
4. Smoking Cessation
Smoking drastically increases heart disease risk by damaging blood vessels and accelerating plaque buildup. Quitting can significantly improve heart health. Resources include nicotine replacement therapies, support groups, and smoking cessation apps. Consult healthcare providers for personalized advice and support plans.

5. Stress Management
Stress triggers increased heart rate and blood pressure, straining the heart. Effective stress management techniques include mindfulness practices, yoga, and regular relaxation exercises, which help lower stress levels and mitigate its impact on heart health, contributing to overall cardiovascular well-being.
6. Moderate Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure and trigger heart rhythm abnormalities. Moderate drinking, defined as up to one drink per day for women and two for men, may potentially offer some heart benefits, but it’s crucial to adhere to these limits to avoid negative health impacts.
Medical Strategies for Managing Heart Disease Risk
1. Regular Health Screenings
Regular monitoring of blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar is essential for preventing and managing heart disease. High readings in these areas can indicate elevated risk factors for cardiovascular complications. Frequent health check-ups facilitate early detection of these risk factors, allowing for timely intervention through lifestyle changes or medication. Early management is crucial as it can halt or reverse the progression of heart disease, reduce the risk of heart attacks or strokes, and enhance overall health outcomes, making these check-ups an indispensable part of maintaining heart health after age 40.
2. Medication Management
When lifestyle adjustments fail to adequately control heart disease risk factors, medications become necessary. Statins are commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol levels by reducing the production of cholesterol in the liver, thereby helping to prevent the formation of artery-blocking plaque. Antihypertensives, including ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers, are used to manage high blood pressure. These medications work in various ways to reduce blood pressure, thus decreasing the heart’s workload and lowering the risk of heart-related events. Discussing these options with a healthcare provider is essential for tailored treatment plans.
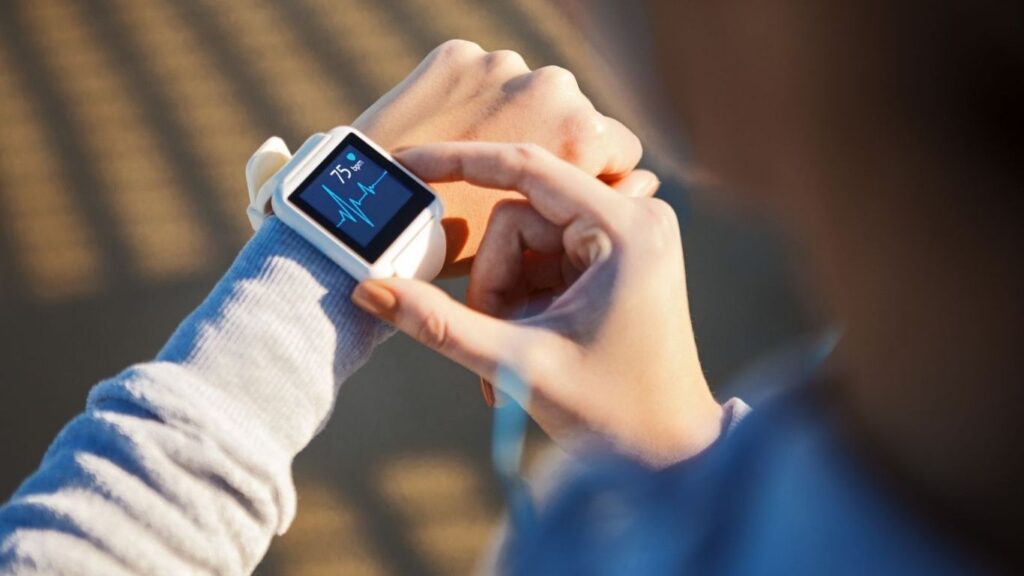
Embracing Technology and Support Systems
In today’s digital age, technology plays a pivotal role in monitoring heart health. Apps and wearables provide real-time data on vital statistics like heart rate, blood pressure, and activity levels, enabling users to make informed decisions about their health. These tools help track progress and alert users to potential health issues before they become severe.
Additionally, support groups and community resources are invaluable for maintaining heart health. They offer emotional support, education, and motivation, which are essential for long-term management of heart health. Engaging with these communities can provide encouragement, share success stories, and disseminate important health information, fostering a collective effort towards healthier lifestyles.

Conclusion
In conclusion, preventing and managing heart disease after age 40 is essential for maintaining quality of life and longevity. By understanding the risk factors, adopting healthier lifestyle choices, and utilizing medical and technological resources, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of heart-related issues. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and cessation of smoking are fundamental steps. Additionally, leveraging technology for continuous monitoring and engaging with support communities can provide the necessary support and motivation. Embrace these strategies proactively to safeguard your heart health and ensure a vibrant, healthy future. Remember, it’s never too late to start taking care of your heart.
Also read: Do Carbohydrates Accelerate Aging? An In-depth Analysis
