Innovation in healthcare is fundamental to advancing medical science and improving the quality of life for millions globally. It serves as the backbone for developing new treatments, improving existing therapies, and ultimately enhancing patient care. This relentless pursuit of innovation has led to breakthroughs that once seemed impossible, transforming the healthcare landscape and setting new standards in medical practice.
Revolutionary medical inventions, in particular, have been pivotal in this transformation. These are not just incremental improvements but are radical, groundbreaking developments that have rewritten the rules of what is possible in medicine. From the discovery of antibiotics that have saved countless lives from infections to advanced imaging technologies like MRI that allow for non-invasive diagnosis, these innovations have not only changed the face of medical treatment but have also significantly extended life expectancy and improved health outcomes across the globe. Each revolutionary invention marks a leap forward in our ability to combat diseases and enhance human health.
8 Most Revolutionary Medical Inventions That Transformed Healthcare Globally
1. Anesthesia
Anesthesia significantly improved patient care, reducing trauma and survival rates during surgery.
The discovery of anesthesia in the mid-19th century marked a monumental milestone in medical history. Before its introduction, surgery was a torturous ordeal with patients often remaining fully conscious. The first successful public demonstration of ether anesthesia in 1846 at the Massachusetts General Hospital revolutionized surgery. This breakthrough drastically reduced the pain associated with surgical procedures, thereby allowing surgeons to perform more complex and longer operations with greater precision. The advent of anesthesia significantly improved patient care, reducing trauma and survival rates during surgery, and has since become an indispensable component of modern medicine, continually enhancing patient comfort and surgical outcomes.
2. Antibiotics
This remarkable drug not only reduced mortality rates significantly but also paved the way for the development of other antibiotics
The discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1928 heralded a new era in medical treatment. Accidentally found when Fleming noticed that a mold, Penicillium notatum, inhibited bacterial growth, penicillin became the world’s first true antibiotic. Its widespread use began in the 1940s, fundamentally transforming the treatment of bacterial infections. Penicillin has saved millions of lives by effectively treating conditions ranging from minor infections to life-threatening diseases such as pneumonia and sepsis. This remarkable drug not only reduced mortality rates significantly but also paved the way for the development of other antibiotics, reshaping the landscape of modern medicine.
3. Vaccination
Vaccines have since played a crucial role in controlling and eliminating many infectious diseases
The development of the first vaccines marked a pivotal shift in public health. Edward Jenner’s introduction of the smallpox vaccine in 1796, using material from cowpox blisters, laid the foundation for immunology. This innovation demonstrated that exposure to a milder disease could confer protection against a more severe one. The widespread use of the smallpox vaccine led to the eradication of the disease by 1980, a monumental achievement in medical history. Vaccines have since played a crucial role in controlling and eliminating many infectious diseases, saving countless lives, and drastically reducing the incidence of formerly widespread and deadly ailments.
4. X-rays
This innovation allowed doctors for the first time to look inside the living body without surgery,
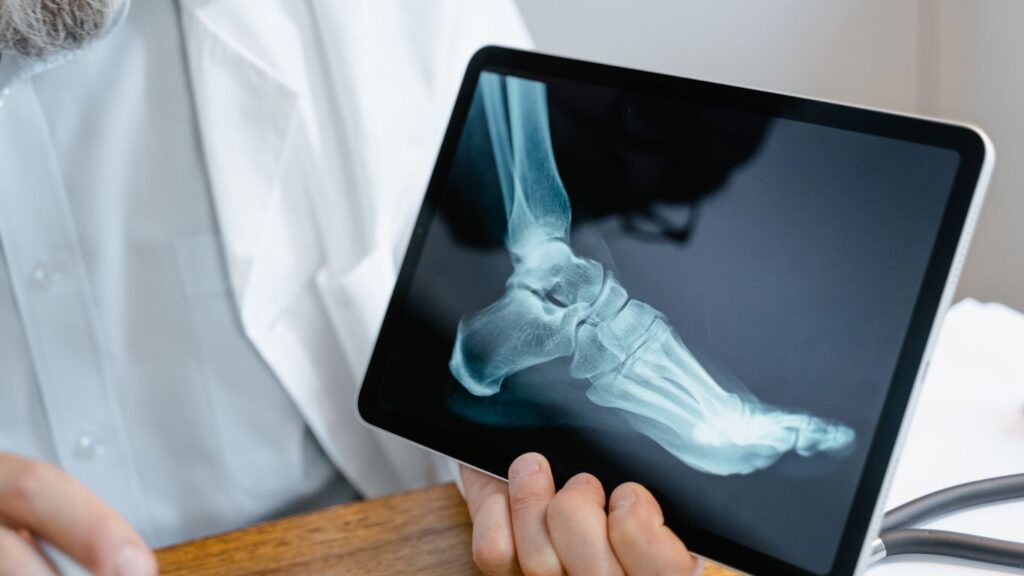
The introduction of X-ray technology in 1895 by Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen revolutionized medical diagnostics. Röntgen discovered that X-rays could pass through human tissue but not bones and metal, creating images that highlighted internal structures. This innovation allowed doctors for the first time to look inside the living body without surgery, drastically improving diagnostic accuracy. X-rays became an essential tool in medicine, aiding in the detection of fractures, locating foreign objects, and diagnosing diseases. Their ability to provide immediate visual insights is crucial for effective treatment planning and has greatly enhanced the ability to manage various medical conditions efficiently and accurately.
5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
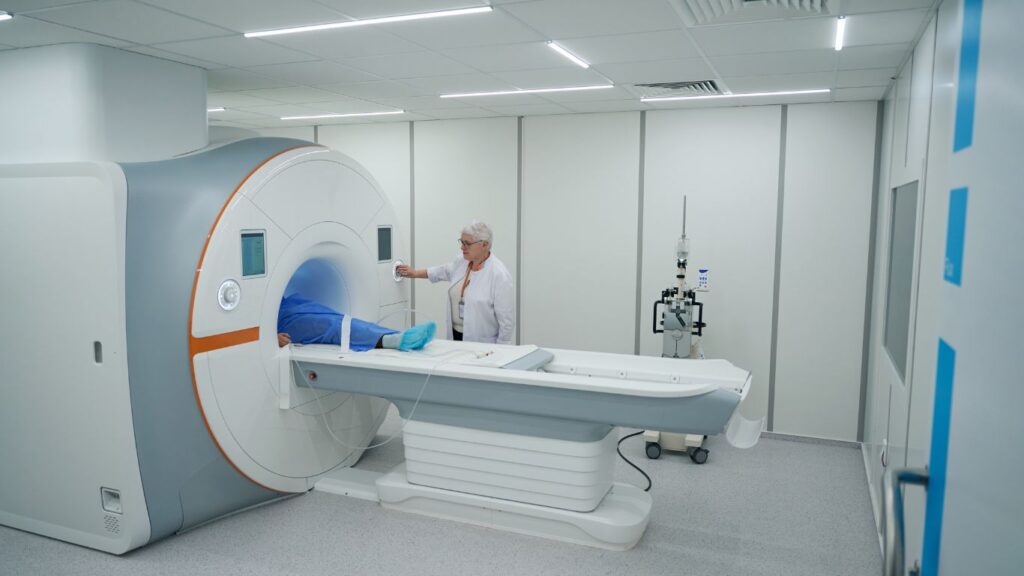
MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) technology, developed in the 1970s, significantly enhanced the capabilities of medical imaging. Unlike X-rays, MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures. This non-invasive tool is particularly adept at visualizing soft tissues, including the brain, muscles, heart, and tumors, with exceptional clarity. MRI is invaluable for diagnosing a multitude of conditions, from brain disorders to internal injuries, providing vital information that greatly aids in accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring. Its detailed imaging capabilities ensure that healthcare professionals can offer more personalized and effective medical interventions.
6. Insulin
Such advancements make daily management of diabetes less intrusive and more adaptive to individual lifestyles
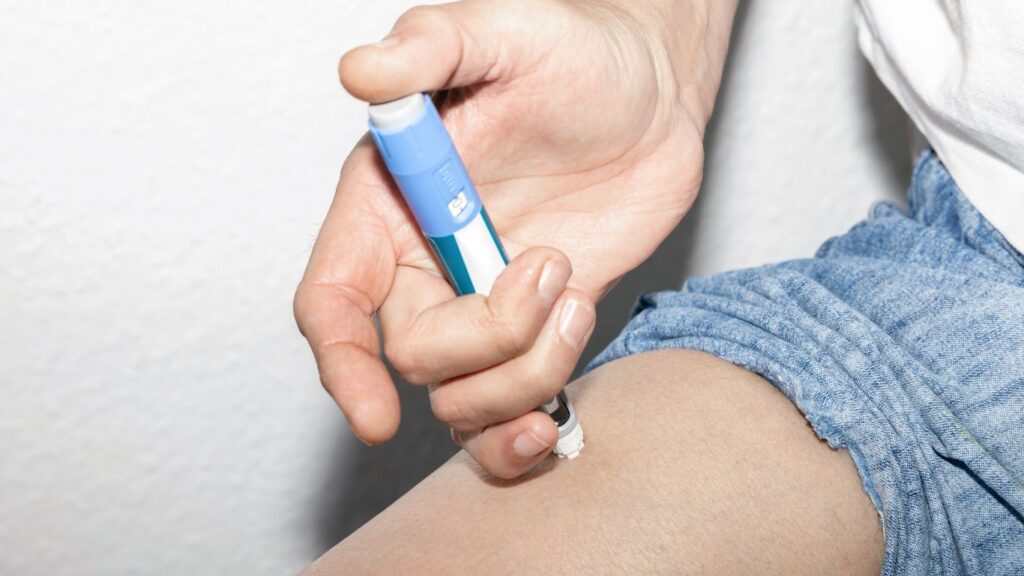
The discovery of insulin in 1921 by Frederick Banting and Charles Best was a lifesaving breakthrough for patients with diabetes, particularly Type 1. Before insulin, diabetes was often fatal; insulin therapy transformed it into a manageable condition. Over the decades, advances in insulin delivery have significantly improved patient quality of life and treatment efficacy. From the original syringes to modern methods such as insulin pens, pumps, and continuous glucose monitors, these innovations offer more precise dosing and consistent blood sugar control. Such advancements make daily management of diabetes less intrusive and more adaptive to individual lifestyles, greatly enhancing patient outcomes.
7. Pacemakers
This small devices are implanted under the skin to help maintain a normal heart rate using electrical impulses
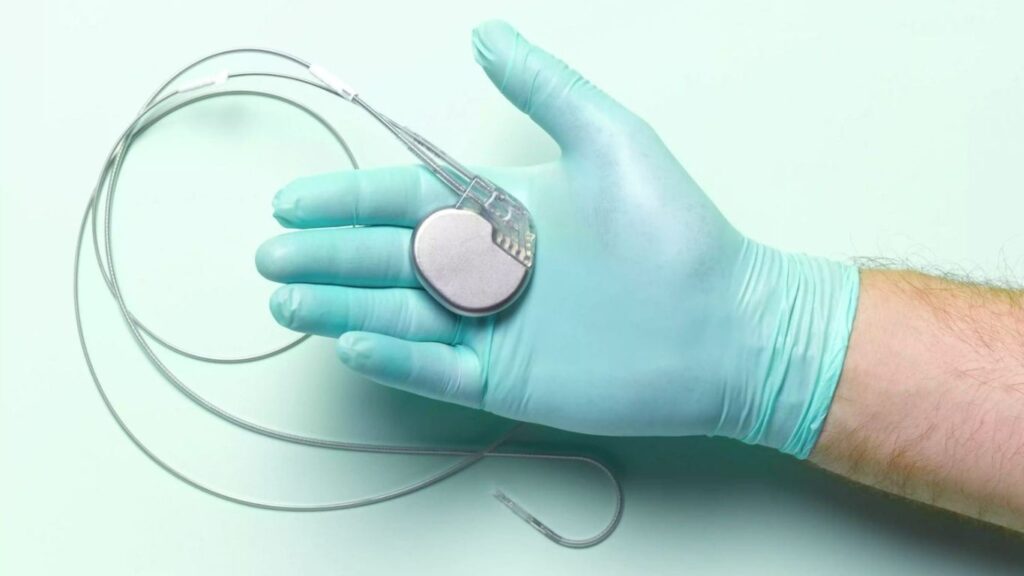
Cardiac pacemakers, first developed in the 1950s, have undergone significant technological advancements, enhancing their efficacy in managing heart arrhythmias. These small devices are implanted under the skin to help maintain a normal heart rate using electrical impulses to prompt the heart to beat at a normal rate. Modern pacemakers are highly sophisticated, capable of adjusting the heart rate to match the body’s activity level, and some are MRI-compatible or even leadless. This development has been crucial for patients with bradycardia or other heart rhythm disorders, improving their quality of life and reducing the risk of heart-related complications.
8. Artificial Heart
It reduce the risk of complications and improve biocompatibility.
The artificial heart represents a remarkable journey in medical engineering, initiated in the mid-20th century. The first successful implantation of a total artificial heart occurred in 1982, serving as a bridge to heart transplantation or as a long-term solution for those who are not transplant candidates. Today’s artificial hearts are more advanced, incorporating materials and technology that reduce the risk of complications and improve biocompatibility. These devices have profound implications for heart disease treatment, offering life-sustaining options for patients with severe heart failure. Ongoing innovations continue to refine their functionality and reliability, promising even greater future benefits.
Final Thoughts
The eight revolutionary medical inventions highlighted in this blog underscore the remarkable journey of innovation in healthcare. Each breakthrough, from the development of anesthesia to the intricate technology behind artificial hearts, has profoundly altered the medical landscape, offering new hope and enhanced life quality for millions around the world. These advancements not only showcase human ingenuity but also reflect a commitment to improving patient care and extending life expectancy. As we continue to face health challenges globally, the legacy of these inventions inspires ongoing research and development, promising an even brighter future for medical science and healthcare delivery.
Also Read: Zinc Supplementation: When and Why It Becomes Necessary