Water is fundamental to life, playing a crucial role in maintaining our health and wellness. Every cell, tissue, and organ in our body relies on water to function properly. From regulating body temperature and flushing out toxins to aiding in digestion and promoting healthy skin, water is indispensable for our overall well-being. However, despite its importance, many of us fail to consume enough water daily, leading to dehydration with varying degrees of severity.
This article aims to shed light on the 10 most common consequences of inadequate water intake, highlighting how such a deficit can impact our physical performance, cognitive abilities, and long-term health. Furthermore, recognizing the importance of prevention, we will provide practical advice on how to stay adequately hydrated. Ensuring sufficient water intake is a simple yet effective step towards maintaining optimal health and enhancing our quality of life.
The 10 Most Common Consequences of Drinking Less Water
1. Energy Levels and Fatigue
Dehydration impairs the body’s energy production by affecting the efficiency of enzymatic activities that are crucial for generating energy. When there’s insufficient water, blood volume decreases, leading to a reduction in the supply of oxygen and nutrients to muscles and organs, which is essential for energy production. This reduction in resource delivery slows down all bodily functions, causing feelings of fatigue and lethargy. Even mild dehydration can have a significant impact on physical performance. It reduces endurance, decreases strength, and increases the perception of effort required for physical activities, making tasks that are usually easy feel much more demanding.
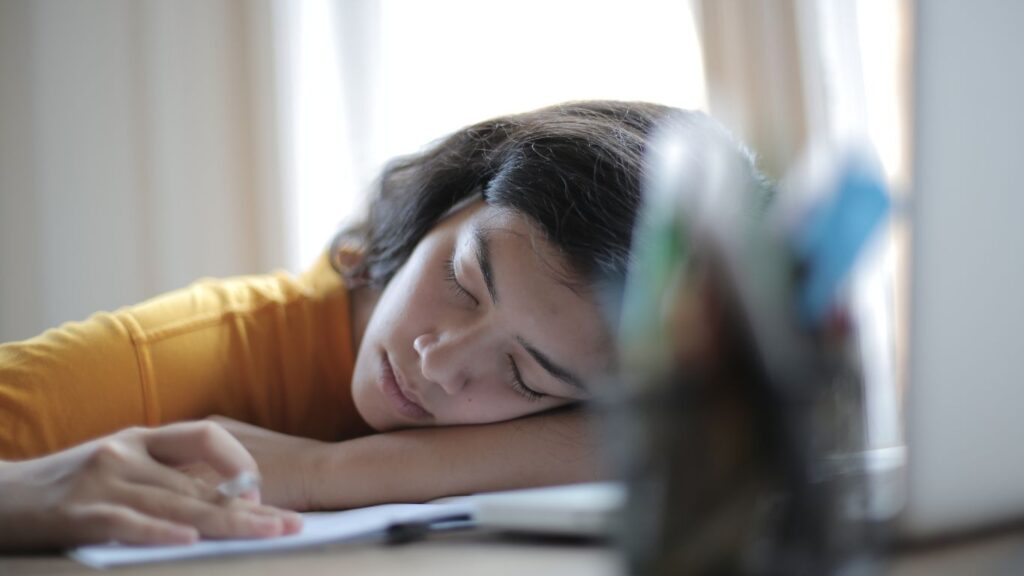

2. Cognitive Function
Dehydration can significantly impair cognitive functions, impacting focus, memory, and alertness. Water is essential for the brain’s optimal performance; even mild dehydration can lead to difficulties in concentration, reduced short-term memory capabilities, and lowered alertness levels. Studies have shown a direct correlation between hydration and cognitive performance. For example, a study published in the “Journal of Nutrition” found that mild dehydration caused by a fluid loss of 1-2% of body weight was associated with decreased concentration, increased perception of task difficulty, and a higher incidence of headaches in participants. This research highlights the critical role water plays in maintaining cognitive health and underscores the importance of staying hydrated for mental clarity and optimal brain function.
3. Digestive Health
Dehydration can severely impact the digestive system, leading to issues such as constipation and an increased risk of acid reflux. Water is crucial for the digestion process; it helps to dissolve fats and soluble fiber, allowing these substances to pass through the intestines more easily. Without adequate water, the intestines absorb more water from food waste, which can lead to harder stools and constipation. Additionally, dehydration can decrease saliva production, which is essential for digesting food and neutralizing stomach acid. Without enough water, the risk of acid reflux may increase as the stomach struggles to digest food efficiently. Thus, staying hydrated is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system, ensuring smooth digestion and reducing the risk of uncomfortable digestive issues.
4. Kidney Function
Inadequate water intake can significantly increase the risk of developing kidney stones and other kidney-related health issues. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering and removing waste from the body, and water is crucial for facilitating these processes. Without sufficient hydration, the concentration of minerals and salts in the urine can rise, leading to the formation of kidney stones. Additionally, a lack of water can hinder the kidneys’ ability to flush out toxins, potentially leading to the accumulation of harmful substances in the body. Thus, maintaining proper hydration is essential for supporting kidney function and ensuring these organs can efficiently remove waste and toxins from the body.
5. Skin Health
Dehydration can have noticeable effects on skin health, leading to dryness, loss of elasticity, and visible signs of aging such as fine lines and wrinkles. When the body lacks sufficient water, the skin can become more vulnerable to these issues, as hydration is key to maintaining the skin’s plumpness, elasticity, and resilience. To support skin health through hydration, it’s essential to drink plenty of water throughout the day and consider using a hydrating moisturizer to help lock in moisture. Additionally, incorporating water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables into your diet can also contribute to overall skin hydration. These simple steps can help maintain your skin’s health and appearance, keeping it hydrated and looking youthful.
6. Cardiovascular Health
Dehydration significantly impacts cardiovascular health by reducing blood volume, which in turn increases blood pressure as the heart must work harder to pump the reduced volume of blood through the body. This additional strain can compromise cardiovascular efficiency, leading to an elevated risk of conditions such as hypertension and heart disease over time. Chronic dehydration can exacerbate these risks, potentially leading to long-term heart conditions. Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for preserving optimal blood volume and pressure, supporting heart health, and reducing the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. It’s a simple yet effective strategy to safeguard your cardiovascular system.
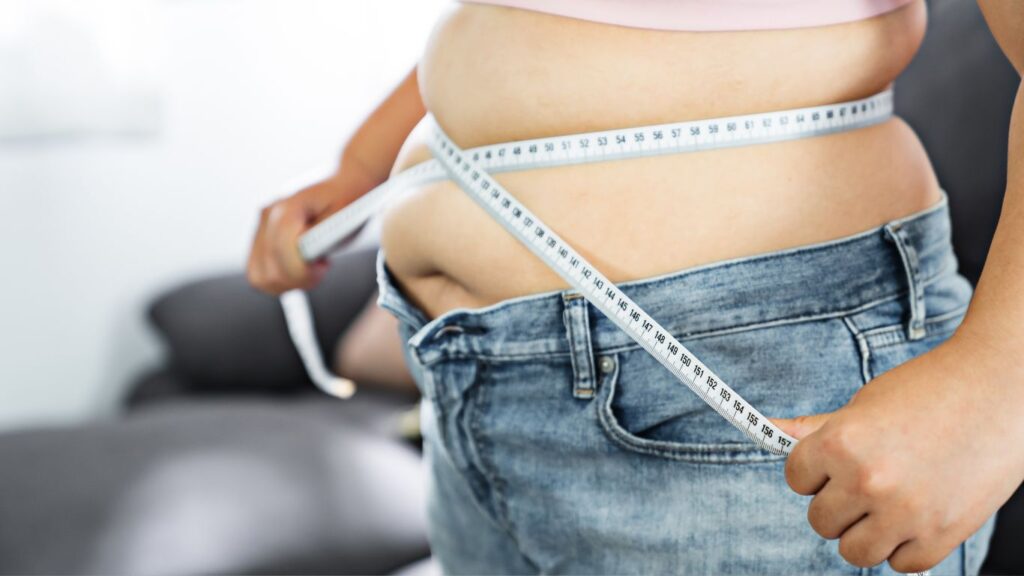
7. Weight Management
Water plays a pivotal role in metabolism and appetite regulation, serving as a key component in the body’s ability to process nutrients and energy. Adequate hydration boosts metabolic rate, which can enhance calorie burning and support weight loss efforts. Furthermore, drinking water before meals can lead to a feeling of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake by minimizing overeating. Studies have shown that people who drink water before meals consume fewer calories and experience greater weight loss success. Staying hydrated is, therefore, not only essential for overall health but can also be a simple and effective strategy for managing weight and supporting weight loss or maintenance goals.

8. Joint and Muscle Health
Water is essential for lubricating joints and maintaining muscle function, as it helps to keep the cartilage around our joints hydrated and elastic, reducing the risk of friction and wear. Additionally, water facilitates the transport of nutrients to muscles, aiding in their proper function and recovery. Dehydration can compromise these roles, leading to joint pain and muscle cramps. Without adequate hydration, muscles may become tight and prone to cramping, while joints might lose their cushioning, leading to discomfort and pain. Ensuring sufficient water intake is crucial for preserving joint health and muscle function, helping to prevent these painful conditions.
9. Immune System Function
Hydration plays a vital role in supporting the immune system and its capacity to combat infections. Water aids in the production of lymph, a fluid in the immune system that circulates white blood cells and nutrients to all body parts, essential for fighting off infections. Additionally, staying hydrated helps to remove toxins from the body, which can improve the immune system’s efficiency. Water also carries oxygen to the body’s cells, facilitating their optimal function and contributing to overall health. Thus, maintaining adequate hydration is crucial for enhancing the immune response and supporting the body’s ability to resist and recover from infections.

10. Mood and Mental Health
Dehydration can have a profound impact on mood, leading to increased feelings of anxiety and irritability. Research indicates that even mild dehydration can affect the brain’s function and mood regulation, exacerbating symptoms of stress and anxiety. A study published in the “Journal of Nutrition” found that dehydration affects neurotransmitter production, which can alter mood and cognitive functions. Furthermore, adequate hydration has been linked to improved mental health outcomes, with participants reporting better mood and decreased levels of anxiety when sufficiently hydrated. These findings highlight the importance of regular water intake as a simple yet effective way to support mental well-being and reduce the risk of mood disturbances.
Practical Tips for Staying Hydrated
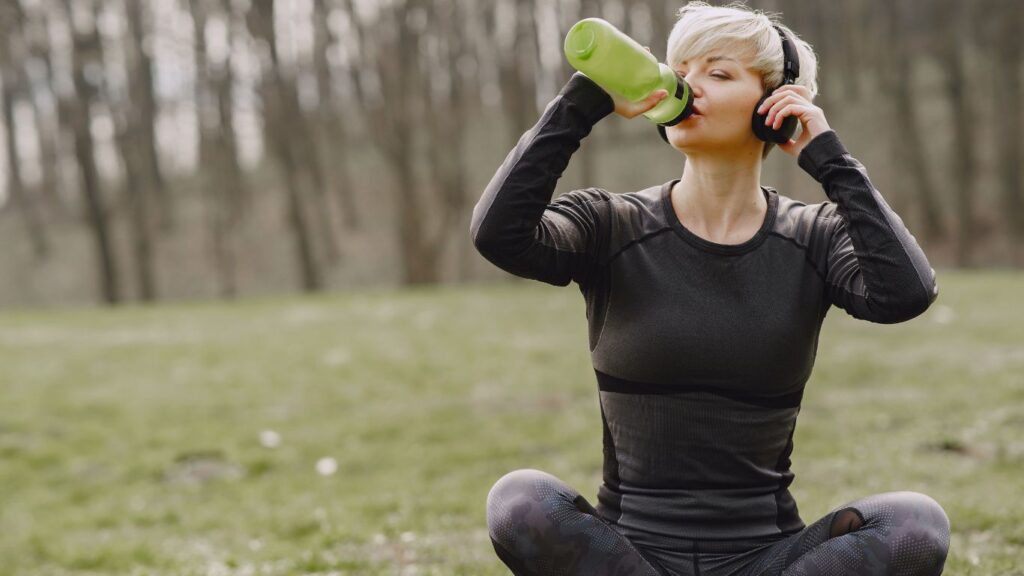

To increase daily water intake, consider carrying a reusable water bottle with you throughout the day, ensuring you have easy access to water at all times. Setting reminders on your phone or using a water-tracking app can help maintain a consistent hydration schedule. Additionally, incorporating foods with high water content, such as cucumbers, tomatoes, oranges, and watermelons, into your diet can significantly contribute to your overall hydration. It’s important to adjust your water intake based on your activity level, the climate, and your individual health needs. For example, during hot weather or intense physical activity, your body requires more water to compensate for increased fluid loss. Listening to your body’s signals and adjusting accordingly can help maintain optimal hydration and support overall health.
Also read: The Multidimensional Health Benefits of Fasting According to Hindu Culture
