Tonsillitis is a prevalent condition that primarily targets the throat of children and young adults, manifesting through swollen and sore tonsils. Recognizing its causes, from viral to bacterial infections, is crucial for effective management. Equally important is identifying its symptoms, which range from a sore throat to fever, to discern when professional medical attention is necessary. While home remedies can provide comfort, understanding when they’re suitable is vital for ensuring proper care and preventing complications. This blog aims to demystify tonsillitis, empowering you with knowledge for better health decisions.
Tonsillitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Home Remedies
What is Tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, two lymph nodes located at the back of the throat. These nodes are part of the immune system, acting as a first line of defense against pathogens entering through the mouth or nose. However, when overwhelmed by viruses or bacteria, the tonsils themselves can become infected, leading to swelling, redness, and pain — the primary indicators of tonsillitis.
The condition can be acute, manifesting rapidly with severe symptoms lasting a short period, or chronic, where infections recur or persist long-term, causing ongoing throat pain and difficulty swallowing. If left untreated, tonsillitis can lead to complications like abscess formation around the tonsils, spread of infection to surrounding areas, or, in rare cases, rheumatic fever or kidney inflammation. Prompt and appropriate treatment is crucial to prevent these potentially serious outcomes.
What is Tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is most commonly triggered by the same viruses that cause the common cold and flu, leading to the majority of cases. These viruses invade and inflame the tonsils, causing the typical symptoms of sore throat and swelling. Bacterial infections, particularly Group A Streptococcus (strep throat), are also significant culprits, requiring different treatment approaches like antibiotics.
Beyond these pathogens, individual risk factors can exacerbate or increase susceptibility to tonsillitis. Allergies that cause nasal congestion and drip can irritate and inflame the throat and tonsils. Environmental irritants like pollution or cigarette smoke can similarly inflame the tonsils. Furthermore, a weakened immune system, whether due to an existing condition or poor nutrition, can make it harder for the body to fend off the pathogens that cause tonsillitis, leading to more frequent or severe infections. Understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
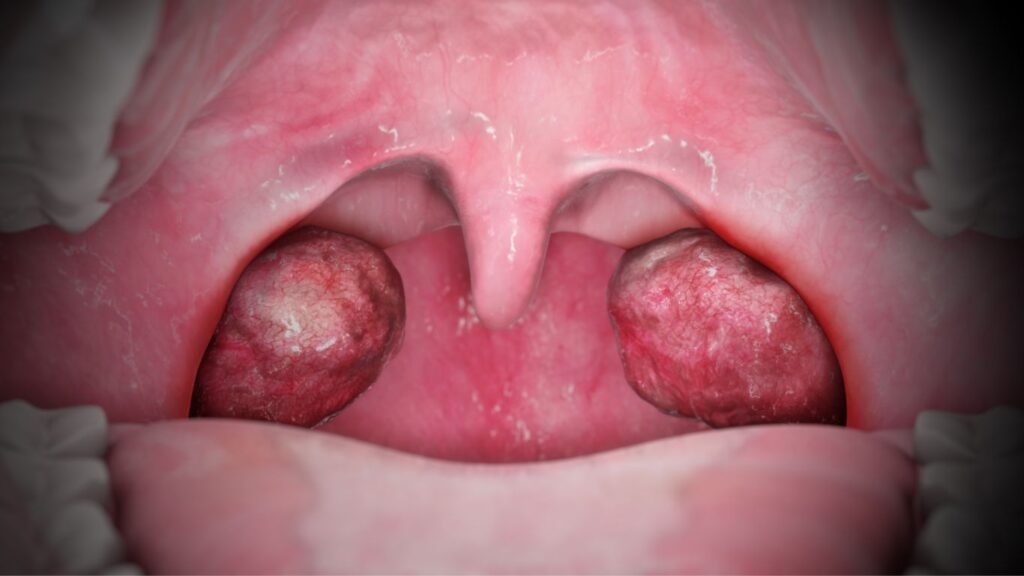
Symptoms to Watch For:
Tonsillitis symptoms often start with a sore throat and difficulty swallowing, as inflamed tonsils can make the act painful. Swollen, tender glands in the neck and a noticeable redness or swelling of the tonsils are common, sometimes with white or yellow spots if pus is present. Fever is a typical response to infection, and bad breath can occur due to the bacteria or virus present.
Viral tonsillitis might present more with coughing and a runny nose, common cold or flu-like symptoms, while bacterial infections, like strep throat, might cause more severe throat pain and swelling without the respiratory symptoms. Recognizing patterns is key; for example, frequent recurrences or symptoms that don’t improve with usual care might indicate a more serious or chronic condition. Persistent or unusually severe symptoms warrant medical attention to prevent complications such as rheumatic fever or peritonsillar abscess.
Diagnosis and Medical Treatments
Home remedies and self-care measures can significantly alleviate tonsillitis symptoms. Gargling with warm salt water several times a day can reduce throat soreness and swelling. Staying well-hydrated helps keep the throat moist and eases swallowing, while warm teas and broths can soothe irritation. Humidifiers add moisture to the air, further easing throat discomfort. Consuming soft, bland foods like yogurt or applesauce can prevent further throat irritation.
Adequate rest is crucial, as it allows the body to focus its energy on fighting the infection. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can reduce fever and alleviate pain. It’s important to avoid irritants like cigarette smoke, which can exacerbate symptoms. While these remedies can provide relief, they’re not substitutes for medical treatment. If symptoms are severe, persist beyond a few days, or are accompanied by difficulty breathing or swallowing, it’s essential to seek professional medical advice.

Prevention Tips
- Regular Handwashing: The cornerstone of preventing tonsillitis and other infections. Wash hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after coughing, sneezing, and before eating.
- Use Hand Sanitizer: If soap and water are not available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer. This can help kill germs when you’re on the go.
- Avoid Close Contact: Keep a safe distance from people who are sick. Avoid close contact, such as hugging or sharing utensils, with those displaying symptoms of a cold or sore throat.
- Don’t Share Personal Items: Avoid sharing drinks, food, or personal items like toothbrushes with others, especially with those who show signs of a throat infection.
- Cough and Sneeze Etiquette: Always cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing. This helps prevent the spread of germs.
- Balanced Diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Nutrients like vitamins C and E, as well as zinc, help boost the immune system.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to keep the throat moist and more resistant to bacteria and viruses.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to boost overall health and immunity.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure sufficient sleep each night, as sleep plays a crucial role in immune function.
- Stress Management: High stress levels can weaken the immune system, so practice stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Avoid Smoke Exposure: Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can irritate the throat, increasing the risk of tonsillitis.
- Keep Surfaces Clean: Regularly disinfect commonly touched surfaces like doorknobs and phone screens to reduce the spread of germs.
- Stay Updated with Vaccinations: Some vaccines, like the flu vaccine, can help prevent infections that might lead to tonsillitis.
- Humidity Control: Use a humidifier in dry environments to keep the air moist, which can help prevent throat irritation.
- Oral Hygiene: Maintain good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, to reduce the risk of bacterial infections in the throat.

Conclusion
Understanding tonsillitis is key to effectively managing and preventing this common yet uncomfortable condition. Recognizing the causes, whether viral or bacterial, and being aware of the symptoms can lead to timely and appropriate treatment. While home remedies can provide relief, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice when needed. By incorporating preventative measures like good hygiene practices and a healthy lifestyle, one can reduce the risk of tonsillitis and ensure better overall throat health. Remember, knowledge and proactive care are your best defenses against the pain and disruption of tonsillitis.
Also read: Understanding Gastroenteritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
